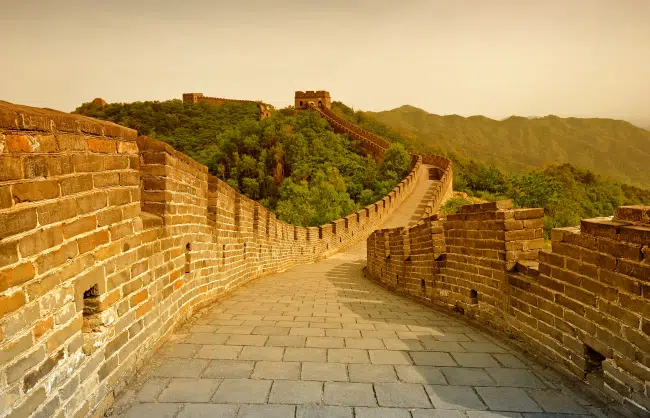
The Great Wall of China is a world-famous icon that attracts millions of visitors to travel to Beijing every year. With a total length of 13,000 miles, it was first constructed over 2,000 years ago. Its construction continued up till Ming Dynasty, when the most significant parts of the Great Wall we know today were built.
The primary purpose of the Great Wall of China was to defend the civilization against nomadic invasions from the north. It served as a protective barrier and provided strategic advantages for defense. So how was the Great Wall of China built? This article will explore the construction materials of the Great Wall of China, methods, and the workers involved in the building of this architectural wonder.

Materials of the Great Wall of China
Rammed Earth and Wood
Because of a lack of technology, before Sui Dynasty (581-618), the main building material of the Great Wall of China was rammed earth. It’s a a technique where a mixture of soil, clay, sand, and gravel is compacted. It was cheap and sturdy, especially in areas with limited resources of bricks or stones. However, rammed earth wasn’t always strong enough against rain and wind.
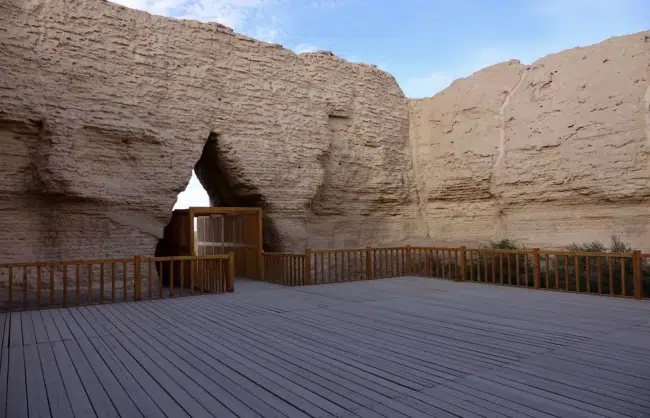
Wood was also a commonly used material of the Great Wall of China. It was mainly used for building the supporting structures, gates, and watchtowers. Different techniques were involved in the constructions in different regions. For example, in the dry climate of Gansu, the section of Jiayuguan Pass was covered in yellow clay for protection.

Bricks and Stone
As technology advanced in Tang and Song Dynasties, brickmaking became much easier. However, bricks were still quite expensive to produce and distribute at the time. It was not until Ming Dynasty when bricks became the primary materials of the Great Wall of China.
Bricks were much more durable and easier to work with than rammed earth. Their rectangular shape was easy for stacking and interlocking, making the structure of the wall much steadier. In Ming Dynasty, the structures of the Great Wall of China become more elaborate with patterns and doorways. The size and weight of bricks made constructions faster.

Bricks and stones were often constructed with other materials to make even stronger. Other Great Wall of China materials include lime mortar, tiles, and even sticky rice. You can see on a Beijing tour that part of the Badaling Great Wall is made of huge stones with lime mortar and sticky rice in its crevices to reinforce the wall.
√ Recommended Great Wall of China tours from Beijing:
- Mutianyu Great Wall Day Tour in Beijing
- 4 Days Beijing Small Group Tour with Jinshanling Great Wall
- 2 Days Beijing Stopover Tour: Great Wall+Forbidden City
- 2 Days Wild Great Wall Trekking & Camping Adventure
Construction Methods Used for Building the Great Wall
Foundation Construction
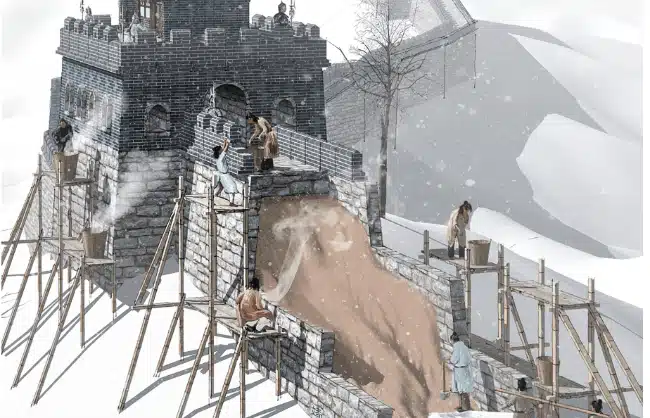
Before building the wall itself, the first thing to do was to establish a strong foundation. Workers dug trenches, lay foundations made of stones and bricks, which would provide stability for the taller structures.
Transportation of Materials
To save costs and manpower, each section of the Great Wall used locally produced materials. There were a number of ways to transport these materials, by manpower, animals, or with simple tools at the time. Workers carried the bricks and stones in baskets and shouldered them. In the winter, they used ice on ground, so it was easier to push or slide the bricks.
Animals that delivered materials included mostly goats and donkeys. Depending on the terrain, people used different types of tools, like wheelbarrows when the construction sites were relatively flat. There were rolling logs and crowbars to transport stones up into the mountains.
Wall Construction
If you go on a Great Wall of China tour today, you will notice that most of the walls are established along the top of mountains. That’s because the natural terrain of the mountains rendered better defensive effects. Layer by layer, bricks or stones were carefully laid on the foundations. Watchtowers and fortresses were built to be vantage points for surveillance or communication.
Who were the Workers that Built the Great Wall?
The building of the Great Wall of China is an immense project that lasted for over 2,500 years. There’s no accurate answer for how many people worked on its construction. The workers involved were mainly three groups of people, soldiers in the army, civilian workers, and criminals.
According to historical records, in Qin Dynasty, Emperor Qin Shi Huang sent about 20% of the country’s population, nearly 1 million people to work on the wall. The wall of Sui Dynasty in Inner Mongolia also took about 1 million people. It’s difficult to make estimations about the rest of the constructions.
Army Soldiers
The main source of manpower for building the Great Wall of China came from the army. It was considered an important duty for soldiers who defended the border. 300,000 soldiers were dispatched in Qin Dynasty, and the project took more than 9 years. Armies were sent to build the wall in Ming Dynasty as well.
Civilian Workers
During every dynasty, whenever the Great Wall was under construction, the court recruited a large number of common people. The number of civilian construction workers was usually in the hundreds of thousands. Emperor Qin Shi Huang recruited more than 500,000 civilian workers. Sui Dynasty even forced the widows to work because so many of the male workers have died in the construction process.
Criminals and Prisoners
Throughout the dynasties, criminals and prisoners were sent to patrol and construct the wall. In Qin Dynasty, they were required to work for 4 years at the wall. The conditions were incredibly harsh, and many lost their lives during the construction.
Challenges Faced When Building the Great Wall
Terrain and Weather
One of the biggest challenges of building the Great Wall of China was the various terrain the massive construction had to take place upon. Workers had to do strenuous labor on tops of mountains, in the deserts, and in extreme weather conditions. They had to adapt construction methods, which required thoughtful planning and engineering expertise.
Logistics and Manpower
For an ambitious project like the Great Wall, the logistics alone posed a lot of challenges. The construction required a large number of materials like rammed earth, bricks, and stones, which were all difficult to transport. In regions where resources were scarce, materials had to be transported from other locations.
The building also required lots of manpower. It was hard to recruit workers because the work was so strenuous and dangerous.
Unexpected Attacks
The primary purpose of the Great Wall of China was to defend the country against invasions from the north, so as constructions took place, workers had to be on guard for sudden attacks from the enemy. They had to protect themselves and their resources as they worked on the wall. There were soldiers constantly on the lookout for potential threats.