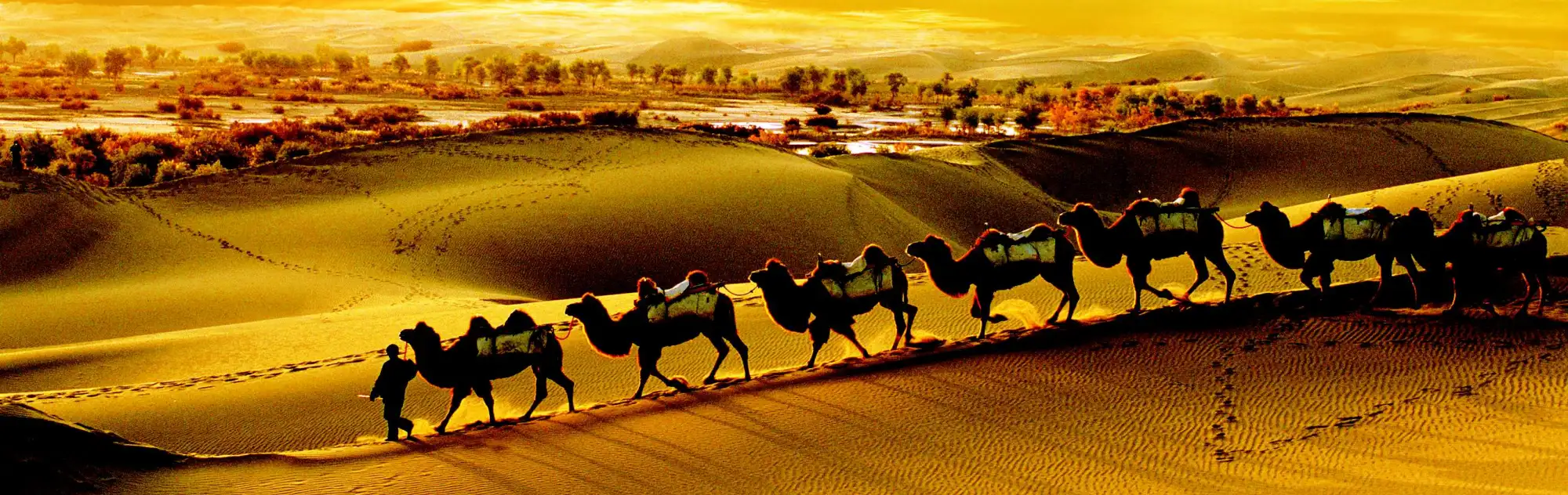
Romanticized as a pathway of adventure, the Silk Road invokes images of camel caravans crossing vast deserts and busy bazaars with a variety of goods. Spanning roughly 7,000 miles, it connected the East and West from China to the Mediterranean Sea. But why was the Silk Road important? Let’s embark on a Silk Road tour through time to uncover its significance.
Functioning as a series of routes for trading goods as well as exchanging ideas, knowledge, and cultures, the Silk Road indeed accelerated the development of economies, cultures, technologies, and many other aspects across continents.
A Thriving Marketplace
The name “Silk Road” was coined in 1877 by German geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen, stressing silk as one of the important goods traded along these routes. Usually referred to as the land Silk Road, it was not a single road but rather a sprawling network of trade routes that connected China to Central Asia, West Asia, and Europe. Moreover, it thrived from about 130 BCE, during the Han Dynasty, to the 1450s CE, when maritime trade routes began to dominate. Read more about Silk Road history.
Starting from Chang’an (today’s Xi’an), many trade hubs rose along the Silk Road, such as the textile markets of Bukhara and Uzbekistan, spice markets in Istanbul and Turkey, and more. Also, silk, spices, precious stones, and tea were commonly-seen goods on the Silk Road. Besides, there was a wide range of valuable goods traded on the routes. Read more about what was traded on the Silk Road.
Recommended China Silk Road Tours
- 7 Days Silk Road Dunhuang-Turpan-Urumqi-Kashgar Tour
- 13 Days Memorable Silk Road Adventure Tour from Xining to Kashgar
- 15 Days Silk Road Tour: Xian-Gansu-Qinghai-Xinjiang-Yinchuan
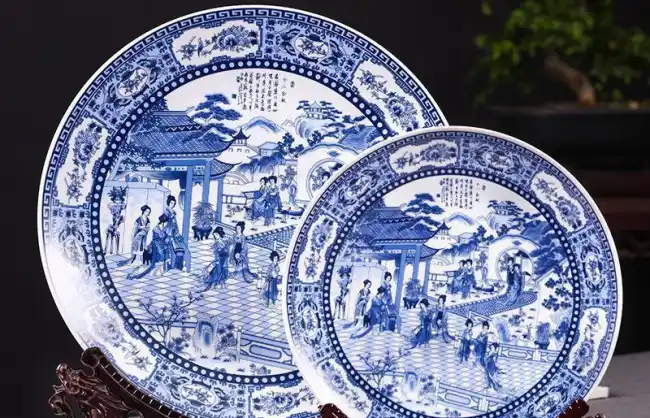

A Meeting Point of Cultures
The Silk Road acted as a bridge for cultural exchange in ancient times. When merchants and travelers started trips on these routes, they carried with them not only goods but also ideas and cultures. Besides, artistic styles and intellectual thought were exchanged along the Silk Road, such as Chinese silk and porcelain, Persian carpets, and Roman glassware, all these were intricate craftsmanship that traveled these routes.
It also fostered the preservation and transmission of cultural heritage, including ancient manuscripts and artistic works. Overall, this gave rise to the documentation and dissemination of cultural and historical knowledge and stopped them from being lost.
A Bridge of Beliefs
The Silk Road paved a good way for the spread of religions, such as Buddhism, Zoroastrianism, Islam, and Christianity. For instance, Buddhism was spread from India to China, Korea, and Japan through the Silk Road by monks and pilgrims as they brought with them sacred inscriptions and religious artifacts.
Besides, the Silk Road enhanced not just the spread of religions but also interfaith communication. Deep dialogues between different religious communities brought about mutual influence and the blending of religious traditions. For example, Buddhism interacted with Confucianism and Daoism when it first came to China and then developed into uniquely Chinese Buddhist schools like Zen Buddhism.
Popular China Silk Road Tours
- 10 Days Ancient China Silk Road Tour from Xian to Kashgar
- 12 Days China Silk Road Tour from Xian to Urumqi by High–Speed Train
- 15 Days In-depth Silk Road Tour from Xian to Xinjiang

A Corridor of Innovation
The Silk Road contributed a lot to promoting technological development in various continents. Through the routes of the Silk Road, innovations such as paper-making, printing, and gunpowder, spread to the West from China and revolutionized their communication, warfare, and daily life.
Apart from technology, scientific enhancement was also a result of the exchange of knowledge. Scholars and scientists from different regions shared ideas and discoveries in fields such as astronomy, mathematics, and medicine through the Silk Road. Besides, scientific texts were translated from Greek and Sanskrit into Arabic and Latin by translators with the bridge of the Silk Road, which enhanced the development of science and technology in medieval Europe.
A Diplomatic Highway
The Silk Road also played an important role in building diplomatic relations. It promoted political relationships between empires and motivated the establishment of diplomatic relations. Besides, ancient empires dispatched ambassadors and signed treaties for mutual relationships through these routes, which helped to maintain peace and formed a sense of mutual respect and cooperation.
The Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE) in China, for example, maintained extensive diplomatic contacts with many other countries and regions, including the Byzantine Empire and the Islamic Caliphates, which contributed a lot to the stability of the region.
As a network of cultural and trade routes, the ancient Silk Road ended its day with huge significance. To marvel at its splendid history and learn more about its rich cultural heritage, you can go on China Silk Road tours to retrace the footsteps of ancient merchants and explorers. Moreover, these tours take you to get close to historical sites, immerse yourself in the cultural performances, and sample the delicious foods in different places along the Silk Road, so never miss them.